Introduction: most visual impairment can be avoided and treated. Identifying asymptomatic patients through preventive screening program and then timely referral and treatment will help reduce the disease burden of individuals and countries. The development of telemedicine, mobile medicine, artificial intelligence and other technologies may provide affordable and high-quality services to remote areas in the next decade, thereby completely changing ophthalmic health care. However, national public health decision makers are faced with the need to maximize the benefits of public health services with limited resources, especially in the post epidemic era. In addition to demand, sustainability, affordability and feasibility, cost-effectiveness is usually a very important consideration. At present, there is a lack of high-quality data and research in this field all over the world. In order to fill this gap and better provide information for relevant departments to make policy and planning decisions, Wang Ningli and Liu hanruo's ophthalmic big data team of Beijing Tongren ophthalmology center comprehensively investigated the health economic impact of Jointly Implementing eye disease screening in rural and urban areas of China from a social perspective. The research shows that the joint screening of AMD and Dr for the whole population aged 50 or above is very cost-effective, Remote screening may be the best strategy in China. This study provides strong data support for strategic consideration and decision-making such as access, landing and pricing of new digital ophthalmic screening technology.

Figure 1: China's first research article on health economics of digital eye disease remote screening was officially published in the latest issue (2022 Jun) of regional health (Western Pacific), a sub Journal of the global authoritative medical journal the lancet, in the form of a cover article. This provides a strong economic basis for carrying out a large-scale joint screening project for a variety of common eye diseases nationwide, and makes the remote screening project a crucial step in clinical transformation and implementation promotion. Scan the QR code to read the original text.
Health economics research on the first population-based digital remote screening of ophthalmopathy in China
Using the method of health economics, this study systematically and comprehensively evaluated the economic benefits of joint screening of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetes retinopathy (DR) in rural and urban environments in China for the first time from a social perspective, taking into account patients, medical institutions and social levels. The results show that in rural and urban China, using traditional face-to-face screening or remote screening for population-based combined screening of AMD and Dr has better cost-effectiveness, and the increased cost of each quality adjusted life year (QALY) saved is lower than the cost-effectiveness threshold recommended by who - three times the per capita GDP.
The study further analyzed the cost-effectiveness of different screening methods (traditional face-to-face screening and remote screening) and screening intervals (1-5 years). The results showed that annual remote screening not only met the cost-effectiveness threshold, but also avoided the most blind years (119 blind years in rural areas and 270 blind years in urban areas), so it became the most recommended screening method. Remote screening can improve clinical efficiency, and the diagnostic accuracy is similar to that of clinicians; It can expand the accessibility and universality of screening; Reduce the burden of repeated clinical tasks, and reduce medical expenses and marginal costs. The rapid development and popularization of telemedicine help to improve the utilization of health and health care services, help clinical diagnosis and treatment decisions, make revolutionary changes in the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases, and bring hope for the realization of large-scale population screening.

Figure 2: the corresponding authors of this study are Professor Wang Ningli and Professor Liu hanruo of Beijing Tongren Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University and Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology, and Professor Tang Jianjun of Renmin University of China. The first communication unit is Beijing Tongren Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University and Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology.
AMD and Dr are the main causes of visual impairment and blindness in the world. In 2020, there were 1.8 million cases of blindness caused by AMD and 860000 cases of blindness caused by Dr in the global population aged 50 and over. As the most populous country in the world, China has a large number of age-related eye disease patients. The latest statistics show that there are 3200 AMD and 2300 Dr related blindness patients in China. With the aging of the population and the increasing prevalence of metabolic diseases, the burden of chronic eye disease will continue to increase. The prevention and treatment of chronic eye disease has brought a heavy economic burden to individuals, families and society, and has become an important public health problem.
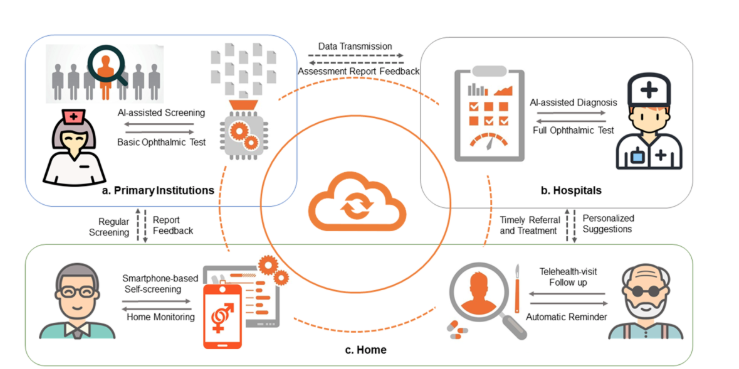
Figure 3: shift from "disease treatment" to "health management" to delay the occurrence and development of diseases to the greatest extent. The medical and health system should not only continue to improve fairness and accessibility, but also lay a good foundation for "national health"; Moreover, we should pay more attention to the problems of systematization and continuity, and realize the real "medical prevention integration" and "upper and lower linkage" through the integration of service system.
In recent years, eye disease screening has become the focus of China's eye health work and the focus of the whole society. The national eye health plan of the 14th five year plan puts forward the goal of "grassroots medical and health institutions generally have the screening ability of common eye diseases". However, due to the large population, vast territory and uneven distribution of medical resources among regions, it is difficult to carry out the regular eye disease screening project for the whole population in China. Whether a public health project is suitable for recommendation and promotion is affected by different economic environment and social conditions, which requires a comprehensive health economics evaluation. Our research results provide favorable data support for the implementation of multi disease remote joint screening in the whole society and the establishment of a national level, complete and sustainable chronic eye disease management system.

Figure 4: the theme of the cover story is "remote digital ophthalmology helps to improve the utilization of health and health care services, help screening diagnosis and treatment decisions, make revolutionary changes in the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases, bring hope for large-scale population screening, and further promote the fair distribution of medical and health resources."

This achievement was officially published in the latest issue (2022 Jun) of regional health (Western Pacific), a subsidiary of the lancet, a global authoritative medical journal, in the form of a cover article. The lancet regional health - Western Pacific, an open access journal under the lancet, is part of the lancet global initiative to promote equal access to quality health care services around the world. The ultimate goal of this journal is to improve the health outcomes of people in the Western Pacific region, and will be committed to promoting the improvement of clinical practice and the progress and development of health policies in the Western Pacific region. Finally, it is expected to improve the health quality of the region and relevant countries. It is committed to promoting the improvement of clinical practice and the progress and development of health policies in the Western Pacific region, and ultimately promoting the improvement of the health outcomes of people in the Western Pacific region. The journal publishes high-quality original research that is expected to improve or inspire clinical practice and health policies in the Western Pacific region, and is an internationally trusted source of clinical medicine and public health knowledge in the Western Pacific region.