There are about 4million people with corneal blindness in China. Corneal blindness has become the second leading cause of blindness. Corneal transplantation is the only means for these patients to recover their eyesight, and it is also the surgery with the highest success rate of organ and tissue transplantation at present. However, postoperative immune rejection is still the main reason for surgical failure.
At present, about 5000 corneal transplantation operations are carried out every year in China. The research shows that the cumulative incidence of rejection once in 10 years after corneal transplantation is 20%, while the incidence of postoperative immune rejection is as high as 60% - 90% in patients with high-risk corneal transplantation such as serious infection and chemical injury.

So what are the main risk factors affecting corneal allograft rejection? Why does Michaels artificial cornea not produce rejection? In this article, we briefly list the types of high-risk factors for you. Today, we will give you a detailed introduction to the main risk factors affecting corneal transplantation rejection and the early warning symptoms and signs of rejection reaction.
High risk factors of corneal rejection
❶ corneal vascularization
Corneal vascularization makes it easier for alloantigens to be presented to the recipient immune system. The survival rate of grafts in non vascular beds is 90%, while that in vascularized beds is only 50% - 75%.
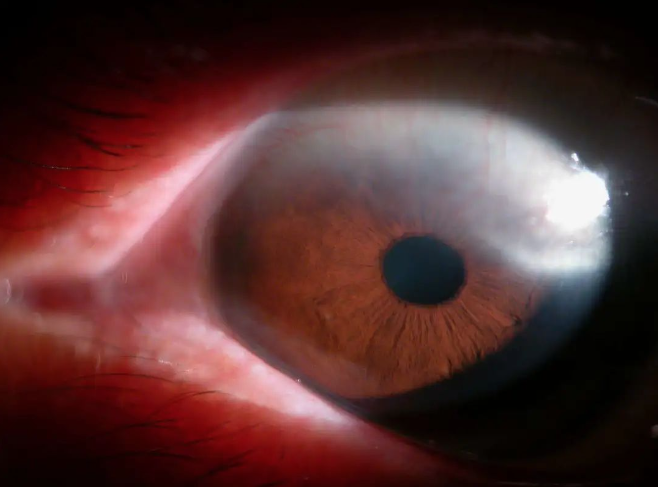
In addition, corneal stromal neovascularization is more dangerous than corneal surface neovascularization, because the risk of corneal transplantation rejection increases with the increase of corneal stromal vascularization. Corneal stromal neovascularization in more than two quadrants strongly predicts the occurrence of rejection.
❷ inflammation of eyes
Ocular inflammation such as blepharitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, uveitis, and endophthalmitis may lead to corneal graft rejection.
Therefore, corneal transplantation should be performed 3 months after the ocular inflammation is still. Epithelial defects after corneal transplantation and suture removal will produce damaging inflammatory reactions. Attention should be paid to prevent immune rejection.
❸ anterior synechia of iris
Whether preoperative or postoperative, anterior synechia of iris may directly expose donor antigens to the immune system, resulting in immune rejection.
Therefore, we should pay attention to the separation of anterior synechia of iris and the formation of anterior chamber during operation, and pay attention to anti-inflammatory after operation to avoid the occurrence of anterior synechia of iris secondary to inflammation.
❹ multiple corneal transplantation
If the patient has undergone many corneal transplantation operations, especially if the operation fails due to graft rejection, it is more likely to cause graft rejection.
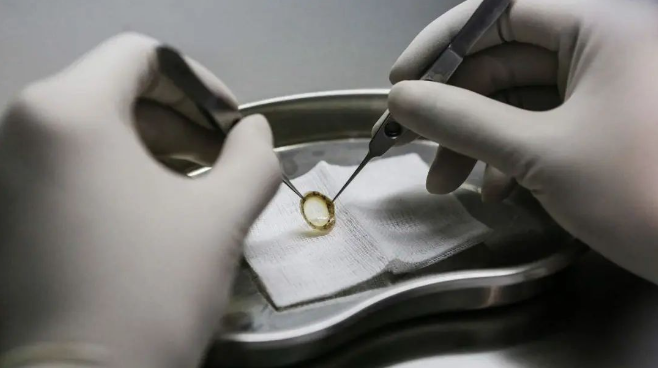
Therefore, the history of anterior segment surgery and vitrectomy can be performed simultaneously with corneal transplantation to improve the incidence of corneal transplantation rejection.
❺ age of patient
Large sample prospective studies have shown that corneal transplant patients younger than 40 years old are more likely to develop immune rejection.
❻ large graft transplantation, partial center transplantation
Both of these conditions make it easier for alloantigens to be presented through the limbal vascular network, resulting in graft rejection.
❼ other factors
Corneal allograft rejection is more likely to occur in patients with a history of glaucoma, chemical injury, and herpes simplex keratitis.
How to detect rejection early
❶ strengthen follow-up
Every patient undergoing corneal transplantation should know the importance of follow-up.
More than half of corneal allograft rejection occurs within one year after corneal transplantation, but corneal grafts, as human allogeneic tissue, have the possibility of rejection for life.
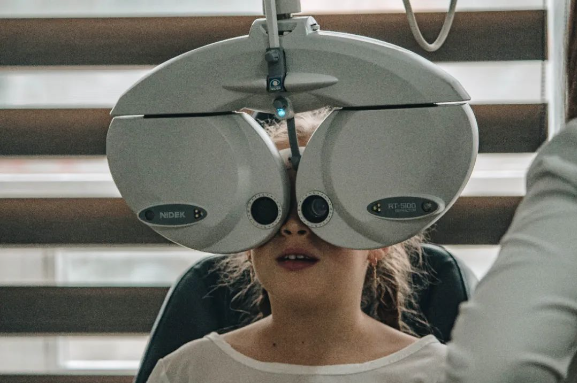
Therefore, regular follow-up, early detection of ocular surface and intraocular abnormalities and even systemic abnormalities that endanger the implant, and timely measures can effectively prevent the occurrence of immune rejection. In case of any abnormal condition, the patient should see a doctor in time to avoid delaying the diagnosis and treatment.
❷ pay attention to four symptoms
Usually, redness, photophobia, decreased vision and eye pain will appear before immune rejection, indicating the occurrence of immune rejection.

Therefore, patients with these symptoms should strengthen follow-up. Once diagnosed, take active and effective treatment measures immediately to protect corneal endothelium as much as possible.
Corneal endothelium cannot regenerate. One time corneal transplantation immune rejection can cause 30% - 80% endothelial cell loss, which is very easy to cause corneal endothelial function decompensation.
❸ pay attention to several signs
Corneal transplantation rejection is a process of immune response, so it has the characteristics of inflammation, such as conjunctival congestion, ciliary congestion, and anterior chamber flicker and cells. These are non-specific signs, but we should be vigilant once they appear. Nonspecific signs also include elevated intraocular pressure and corneal epithelial defect.
Subcutaneous infiltration on the graft is also a precursor of corneal transplantation rejection. It occurs in 10% - 15% of corneal transplantation immune rejection. It is the infiltration of inflammatory cells under the epithelium, which does not affect the graft bed, and the treatment effect is good without leaving scars. However, if it is not treated in time, corneal transplantation rejection will "erupt in an all-round way".