Source: Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center
"Pre retinal neovascularization" is a common pathological feature of a common clinical disease, such as diabetic retinopathy, with a high rate of blindness. Different from other retinal choroidal neovascularization, it grows at the interface of retina and vitreous. Vitreous collagen matrix is an important microenvironment for its occurrence and development. Exploring the internal mechanism of collagen promoting neovascularization is an important research basis for exploring its specific targeted therapy.
Based on the previous research on "vitreous collagen promoting neovascularization and opticin regulation target", Professor Ma Jin team of Zhongshan ophthalmology center creatively revealed the inhibitory effect of endogenous and exogenous opticin expression on preretinal neovascularization through optc overexpression plasmid transfection and intraocular injection based on the zebrafish retinal neovascularization model induced by hypoxia (Fig. 1), Through in vivo mass spectrometry analysis and in vitro simulation experiment, the "collagen gxxger integrin" was successfully revealed α The formation of subunit I domain complex and the important role of RhoA / Rock1 pathway in the inhibition of neovascularization by opticin (Fig. 2) reveal the effect of glycoprotein opticin on the surface of vitreous collagen on preretinal neovascularization and its mechanism, so as to uncover the mystery of the collagen specific domain promoter of the disease, And provide direction for corresponding targeted therapy.

Figure I
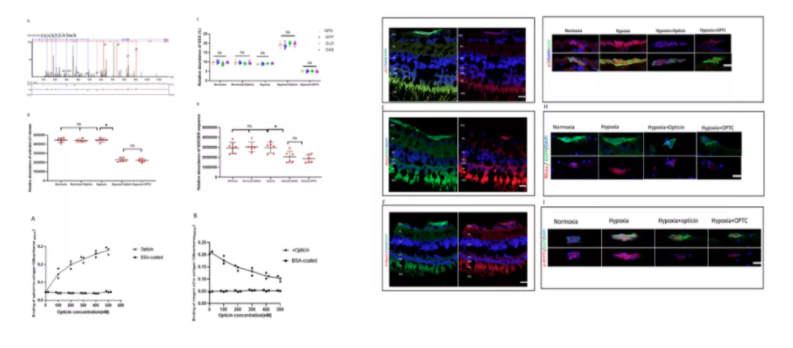
Figure II
On this basis, the research group continued to explore a reasonable way for the targeted intervention of the disease. In vivo and in vitro studies revealed for the first time that the extract maolanin can inhibit α 2 and β Integrin 1 binds to collagen domain and inhibits the formation of preretinal neovascularization by activating RhoA / Rock1 pathway (Fig. 3); In the comparison of adult fish and embryonic fish in the hypoxia induced zebrafish model, it is perfectly demonstrated that the intraocular vitreous collagen microenvironment is an important promoter for maolanin to exert its effect, and the hypothesis that the collagen microenvironment is a necessary condition for maolanin to exert its anti neovascularization in the eye is put forward for the first time (Fig. 4).
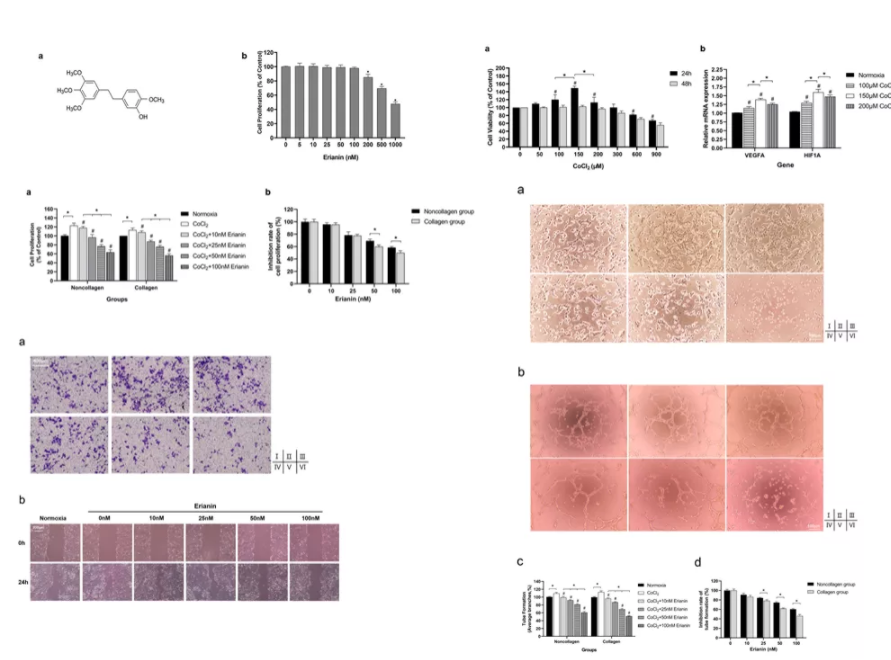
Figure 3
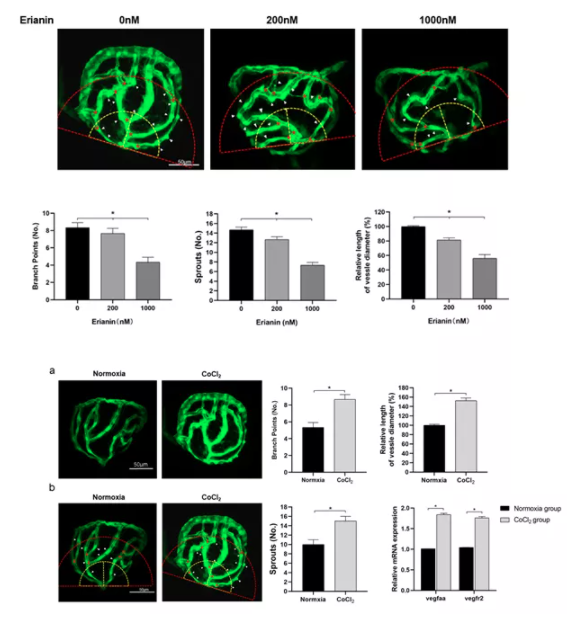
Figure IV
So far, the action mechanism and regulation of "vitreous opticin protein" and "extract maolanin" of Professor Ma Jin's team in collagen promoting anti preretinal neovascularization have been gradually clear, which has opened the mystery for the prevention and treatment of this kind of disease.
The two papers of this series of studies were published in the same issue of the authoritative ophthalmology journal Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science (IOVs) (January 2022), respectively entitled "opticin ameliorites hypoxia induced retinal genetics by suppression of integrity" α 2-I domain – collagen complex formation and RhoA / rock1signing "(corresponding author is Professor Ma Jin, and doctoral students Liu Xiaoxue and Xing Yue are the co first authors) "Erianin controls collagen mediated retinal genetics via the RhoA / Rock1 signaling pathway induced by the alpha 2 / beta 1 integral collagen interaction" (corresponding author is Professor Ma Jin, master's student Li Xueke and doctoral student Liu Xiaoxue are the co first authors).
Sun Yat Sen ophthalmology center and State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology of Sun Yat sen University are the only units.

Original link:
https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2778244
https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2778297