Vision of Zhongshan Eye Center
On March 25, Professor Zhuo Yehong / Su Wenru team of Zhongshan ophthalmology center of Sun Yat sen University published the title "TNF" in the international famous journal biomaterials- α Stimulation enhances the neuroprotective effects of retinal MSCs derived exosomes in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury via the meg3 / mir-21a-5p axis ", which reported that the exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells are rich in mir-21a-5p, which can protect retinal nerve cells from injury, and TNF was found for the first time- α Pretreatment of stem cells can enhance the neuroprotective effect of their exosomes, provide a new treatment strategy for retinal nerve cell injury, and propose a scheme to enhance the efficacy of exosomes.


Neuroblinding eye disease has the characteristics of irreversibility and high blindness rate, which has a serious impact on patients, families and society. It has always been a worldwide problem to be solved. Ischemia, hypoxia, inflammation and other factors cause irreversible damage to retinal nerve cells. Although a large number of studies have tried to find effective treatment, the effect of potential neuroprotective drugs in phase II / III clinical trials is not ideal, and they still can not prevent or reverse nerve injury. Up to now, there is still a lack of safe and effective treatment methods, so it is urgent to find new treatment ideas.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSc) are widely distributed pluripotent stem cells with immune regulation, microenvironment regulation and post injury repair. Previous studies have confirmed that MSC can effectively treat a variety of diseases, but the potential safety problems of MSC still hinder its wide use in clinic.
MSC can play an immune regulatory role through paracrine mechanism. As a subcellular component secreted by MSC, MSC derived exosomes can play a biological effect as a paracrine factor of MSC, which provides a new way to further realize cell-free therapy. Exosomes are membranous vesicles released into the extracellular matrix after the fusion of intracellular multivesicles and cell membrane, with a diameter of 30-150 nm. It contains proteins, mRNA, miRNA and other substances, which are widely involved in the communication between cells. In this study, MSC derived exosomes (g-exo) were injected into vitreous cavity and applied to the treatment of retinal injury. It was found that it can regulate immune inflammatory response and protect retinal ganglion cell (RGC) injury. And TNF was found for the first time- α Pre stimulation can enhance the protective effect of MSC derived g-exo (TG exo).
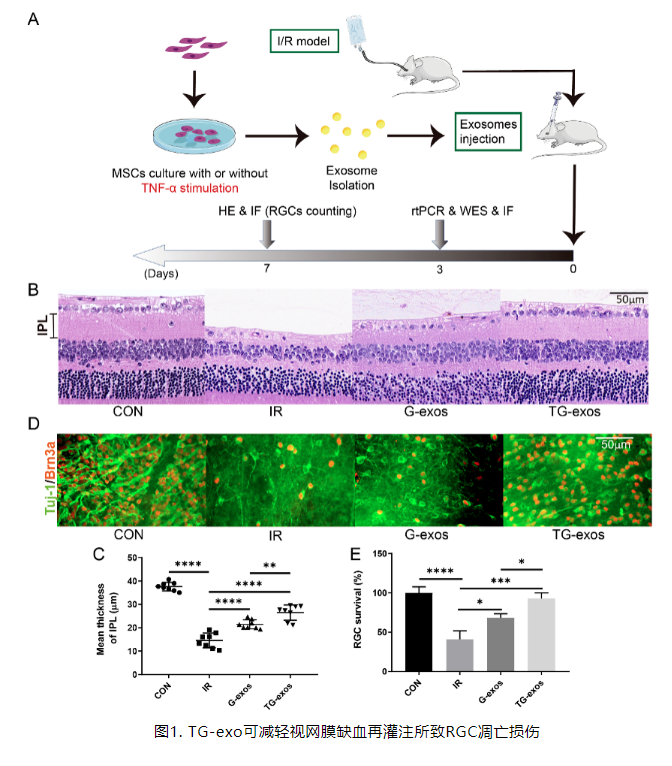
Figure 1 TG exo can reduce RGC apoptosis induced by retinal ischemia-reperfusion
In vivo and in vitro models, it was further found that mirna-21-5p rich in g-exo could protect RGC injury and inhibit microglia activation.
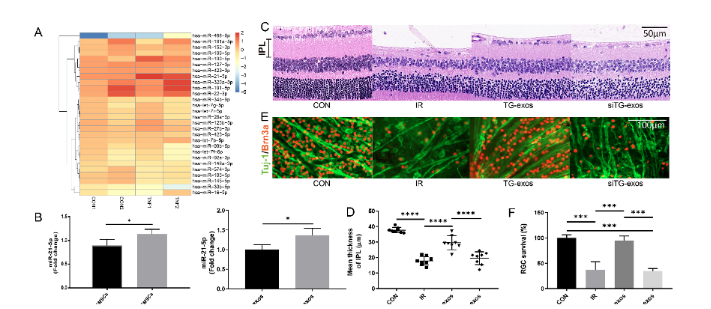
Figure 2 Mir-21-5p in TG exo mediates the protective effect on retinal injury
Further, the researchers predicted and verified the upstream meg3 and downstream target protein PDCD4 of mirna-21-5p. It was confirmed that meg3 / mirna-21-5p / PDCD4 signal axis mediated the neuroprotective effect of TG exo on retinal injury.
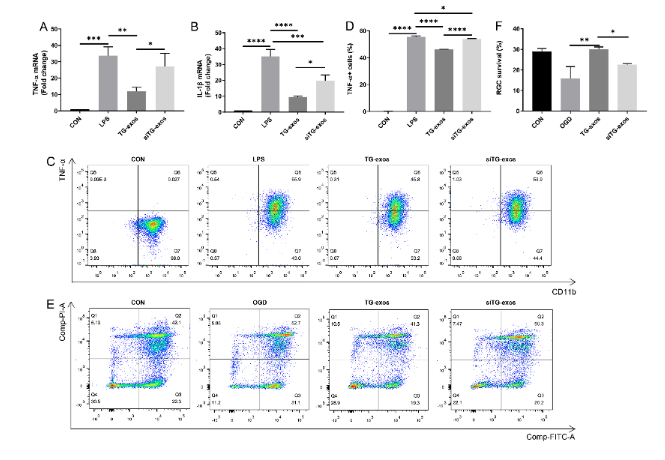
Figure 3 Mir-21-5p in TG exo mediates the inhibition of inflammation and the protective effect on RGC
In conclusion, this study reported that the exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells are rich in mir-21a-5p, which can protect retinal nerve cells from damage, and TNF was found for the first time- α Pretreatment of stem cells can enhance the neuroprotective effect of their exosomes. It provides a new treatment direction for the treatment of retinal nerve injury, and provides a scientific basis and basis for the clinical transformation of MSC derived exosomes in neuroblinding eye diseases.
The research of the project has been supported by the national key R & D plan and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Sun Yat Sen ophthalmology center and State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology of Sun Yat sen University are the first units. Dr. Yu Ziyu is the first author of this paper. Professor Zhuo Yehong, Professor Su Wenru and Dr. Zhu Yingting are the corresponding authors of this paper.
Original link:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961222001235#ack0010