As we all know, although the cornea is in a relatively immune "amnesty" state, and although corneal transplantation is the most successful operation among many organ and tissue transplantation operations, the probability of corneal transplantation failure is still high due to the existence of postoperative immune rejection, especially after high-risk corneal transplantation (neovascularization, multiple corneal transplantation and active inflammation), the immune rejection is as high as more than 50%.
It can be said that immune rejection after corneal transplantation is a devil like complication for corneal transplant patients, because they are likely to become blind again or even for life.

It is gratifying that although the immune rejection after corneal transplantation is a complex multifactorial process, with the development of modern molecular immunology, scholars' understanding of its mechanism is deepening, and it has been confirmed that the following risk factors can lead to corneal transplantation rejection ☟ ☟
① Corneal vascularization
② Autoimmune diseases
③ Inflammation
④ Chemical injury
⑤ History of multiple corneal transplantation
⑥ Age
⑦ Large graft transplantation, partial center transplantation
⑧ History of glaucoma
⑨ Anterior synechia of iris
Among them, corneal neovascularization is a major risk factor. So today, let's talk about the relationship between corneal neovascularization and corneal transplantation rejection.
Normal cornea is transparent and avascular. The avascular state of cornea is based on [low levels of angiogenic factors and high levels of anti angiogenic factors], which is an important factor in maintaining corneal transparency and serving as an important refractive stroma.

However, due to various pathogenic factors, such as severe chemical burns, inflammation, infection, and degeneration, the balance between these two factors is broken, and tends to promote angiogenesis, the avascular state of the cornea will change, and neovascularization will grow from the limbal vascular network. At this time, the rejection rate and the failure rate of corneal transplantation increase at the same time.
The study found that if there were neovascularization or abnormal vascular growth in the recipient cornea before operation, the failure rate of corneal transplantation increased significantly by 30%.
It should be noted that not only pre-operative corneal neovascularization can affect the survival of the graft, but also post-operative neovascularization can significantly affect the survival rate of the graft.
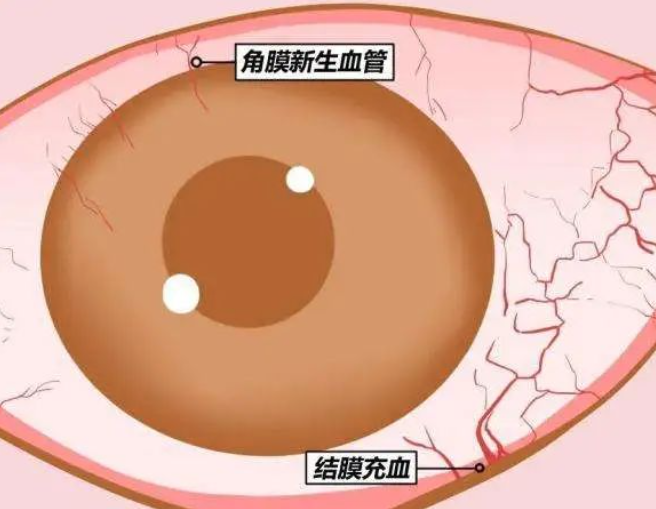
Because even if corneal transplantation is performed on a non vascular graft bed before surgery, corneal neovascularization will occur after surgery, and there will also be a probability of immune rejection.
It is no exaggeration to say that once new blood vessels grow out of the cornea, it means that there will be immune rejection after corneal transplantation.
However, the cornea with neovascularization will not cause any adverse effects on the Microk transplantation, and for the Microk, it and neovascularization belong to the "two-way rush".
Some scholars found in the clinical experiment of Microk: in the whole process of corneal vascularization, the scaffold exists stably between corneal layers, and the edema gradually subsides. There is no pathological damage such as exudation and necrosis, such as those in some clinical diseases with neovascularization, no complications such as corneal dissolution and leakage, and no formation of corneal leukoplakia. The artificial cornea scaffold has no adverse effect on the long-term nutrition and metabolism of the cornea, It has good biocompatibility.

Why is this?
It turns out that different from corneal transplantation, artificial corneal stents often need good vascularized corneal conditions in clinical applications.
The neovascularized corneal graft bed is beneficial to the artificial cornea. It can provide a good microenvironment for cell proliferation and migration, promote cell proliferation and collagen synthesis, reduce postoperative corneal lysis and the excretion rate of the artificial cornea, and is conducive to the stable targeting of the artificial cornea.
Research on corneal transplantation also shows that the existence of neovascularization does not hinder tissue healing. On the contrary, granulation tissue in the early stage of healing accelerates the healing process. Transplant rejection is simply because the presence of neovascularization provides an opportunity for donor antigens to contact host lymphocytes.

In addition, various factors released by moderate inflammatory reaction after Microk implantation can promote neovascularization, activate corneal cells and grow into scaffold pores, which is an important factor for maintaining the stability of Microk.
With the deepening of the research on corneal neovascularization in recent years, the inhibition of immune rejection will find a new breakthrough.
At the same time, Microk is also worth discovering in combating the immune rejection caused by corneal neovascularization, especially in high-risk corneal transplant patients, such as corneal blindness caused by chemical injury, thermal burn and explosive injury. Of course, we will also send you the first-line news of products and enterprises in time, so that you can know Michal faster and more conveniently.